Becoming a parent is an extremely special time that brings both great joy and new challenges for expecting parents, such as pregnancy pain, fear of childbirth pain, and the strain carrying one’s newborn.
Read moreCompassionate Dispassion
I know I'm not alone in feeling that at this moment in time and history, I need all my self-care skills and then some. The Alexander Technique is at the top of my list.
Read moreConfession of a Prejudiced Woman
Full disclosure: I marched against the Vietnam War years ago and much later against the war in Iraq. I eat kale and arugula. I volunteered and voted for Hillary Clinton, and have been in mourning ever since election day. Having said that, I will add that this is not a political blog!
Read moreBody Mapping and the Alexander Technique
I began my relationship with Body Mapping in my early days as a college music student, little did I know how much of my future would be determined by simply registering for this course that came so highly recommended.
Read moreAlexander Technique at Political Demonstrations
I’m not advising you on who or what to protest, but I marched on Sunday at a big anti-Trump rally in Midtown Manhattan. As I was remembering my Alexander principles, I came up with a few guidelines for participating in the demonstration or march of your choice.
Read moreRiding the Wonder Wheel at Coney Island: How to manage a fear of heights with the Alexander Technique*
 by Brooke Lieb
*I recommend NOT riding the ferris wheel in the first place, but if you do find yourself having to manage your fear of heights, at least you might be able to ease some of the discomfort.
by Brooke Lieb
*I recommend NOT riding the ferris wheel in the first place, but if you do find yourself having to manage your fear of heights, at least you might be able to ease some of the discomfort.
In early August 2016, I joined a friend of mine on her birthday adventure to Coney Island. There were three other friends joining us, and the five us rode the F train to the last stop. Our first stop was the 150 foot high Wonder Wheel. The birthday person vetoed the moving cars, the ones that swing along the spokes, towards and away from the center of the wheel, in favor of a stationary car, which had instructions “Do Not Swing This Car” repeatedly posted outside the ride and inside our car.
We bought a discount ticket – Five rides for $30.
There was no line, and there weren’t many people on the ride. That would mean less stops as riders got off and on, so this would be over soon enough.
I got in the back with one other woman, and our Birthday person and her two remaining friends got in front.
My seat companion began to tense up the moment we began our ascent. She expressed her discomfort at heights, and I could see she was starting to panic, just a bit.
“I don’t like heights, either” I said. “This is what we’re going to do. Let’s both move into the middle of the car. Look down at the floor, at our feet. I’m going to hold your hand, and we’re going to breath together. I bet your heart is pounding like a scared rabbit in your chest, I know mine is!”
“Yes, it is…” she said.
“Now, as you’re breathing, if you can think about releasing any tension at the nape of your next, that can help to.”
We managed to look out at the view, part of the time. We kept periodically stopping, rocking in the air and hearing the creaking sound of metal as riders were let off and on the ride. There was no way I could pretend this wasn’t happening.
I held my seat mate’s hand, and tried to see what else was happening, as I took comfort in knowing I would with another being at the moment of my death if this car came off and plunged to the ground. (Yes, I was ABSOLUTELY having those kinds of thoughts!)
Our birthday person’s two friend in the front were doing well, though she wasn’t so keen on it…
One woman had her selfie-stick out and was snapping shots of all of us and the view. The other woman, sitting in the middle, was very easy going and relaxed. Clearly, these two weren’t experiencing anxiety like the rest of us.
“You have a very calming effect” my seat mate said.
“Doesn’t she?” my friend replied.
As we began our descent of the first rotation, my friend speculated “Maybe we only go around once…” with hope.
Coming down didn’t bother me at all, and my anxiety immediately receded as we finished our first rotation. When we didn’t stop, heading up again, my friend said “Well, then it’s only two rotations, because it’s not too busy.”
I was surprised by the return, in full force, of my pounding heart, fluttering stomach and general discomfort as we headed up for the second round. My seat mate was just as uncomfortable as she had been during our last trip up.
We did talk about our discomfort throughout the ride, and the other women were sympathetic to our reactions. It strikes me, in retrospect, that it must’ve helped that we didn’t have to contend with either teasing or well intentioned attempts to calm us with intellectual reasoning. There is nothing intellectual about this fear response.
Once we were on our descent for the second and thankfully final revolution, my anxiety dissipated and was gone by the time I embarked from the ride.
What has the Alexander Technique got to do with this story?
It is my long time study of the Alexander Technique that gave me the skill to summon my inner resources in the face of a frightening experience. I have learned how to stay more present in moments when I have historically panicked.
Part of my skill as a teacher of the Alexander Technique allows me to teach others to summon their inner resources, and the act of teaching gets my attention off my own internal reaction to things that trigger me. Taking care of my student, by teaching and modeling this self-soothing, is best taught by me actually self-soothing as I teach. It’s a win-win.
Alexander calls this self-soothing skill “inhibiting” – that is, interrupting a habitual cascade of responses to a trigger (Alexander referred to it as a stimulus), in order to stay more present to assess the current situation more accurately, in order to respond more appropriately to this moment, in this moment.
I have an old whiplash injury, so any abrupt impact, whether it’s front-to-back or side-to-side triggers my injury.
I skipped the kiddy rollercoaster, I don’t ride any rollercoasters, and I don’t do water rides.
I do fine with spinning rides, so bring on the Merry-Go-Round!
I know I can survive the Ferris Wheel, so if someone offers me a good enough incentive (I am seeing a $ with at least 3 zeros after it…) I can do it, but otherwise, there’s no reason for me to EVER ride one again…
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Being A “Yes" to Life, Without Losing My Reason
 by Brooke Lieb
I have been involved in business and life coaching and spiritual communities that were all about being a yes. “Being a Yes” means looking on the positive side of things, going for it, not taking no for an answer, and with that, the dark underside of self recrimination, FOMO (fear of missing out), shame if I’m not being a yes, and the uncomfortable feeling that comes when you say yes in times when a “no” is more authentic.
by Brooke Lieb
I have been involved in business and life coaching and spiritual communities that were all about being a yes. “Being a Yes” means looking on the positive side of things, going for it, not taking no for an answer, and with that, the dark underside of self recrimination, FOMO (fear of missing out), shame if I’m not being a yes, and the uncomfortable feeling that comes when you say yes in times when a “no” is more authentic.
Over the years, I have come to recognize I have a number of patterns and cycles that are starting to feel out of balance. There have been long periods of time, years or more, when I have been in some form of business or life coaching, or trying different systems and strategies to create results in my personal or professional life, focusing on fitness, focusing on diet, shifting from one system to another. I have read hundreds of self-help books, and have been more or less systematic over the years at making steps to move towards having the life I think I want. I have been fortunate, with good health, access to education, employment and enough success to call my passion for the Alexander Technique my profession. I have experienced very few tragedies or economic challenges that caused me any prolonged stress. I don’t know how much of that is the result of my good fortune, good decisions, or my perception or interpretation of events and circumstances. I don’t know how much is because of how the Alexander Technique has given me access to my reason.
Even with all of that, my tendency is to avoid risk, keep my life simple and operate in a small orbit. I have many stories and rationalizations for why I don’t or can’t do certain things, and there are a lot of “no’s” in my moment to moment choices. I don’t mean saying no to a stimulus, I mean habitually saying “no”.
It ends up being an ongoing balancing act. Too many yes’s or too many no’s tend to throw me out of balance. Too many yes’s, and I can end up overcommitted, spread too thin, exhausted, coming up short, pushing too hard and irritable. Too many no’s, and I may start to feel lonely, isolated, and as though I am not taking advantage of what life has to offer.
How does the Alexander Technique help?
I have a process to assess where I am and what I am doing in the short and long term. If I consider "the need to choose" as a stimulus, the rest of Alexander’s process is consistent. Pause, inhibit my habitual response to “choosing”, send my directions, continue to send my directions while considering my choice in this more integrated state, and move forward. In the case of a decision, I may need to reevaluate and reassess as the choice plays out over time.
My choice may yield an unsuccessful outcome, but if I continue to work with Alexander’s process, I can make a new decision, change my strategy, and seek additional information to assist in how I respond to the outcome. There is always a new stimulus, there are always more moments of making decisions.
I am not implying that I, or anyone else, NEEDS the Alexander Technique in order to access what I have described here, and find balance in the moment. I don’t know, however, how it happens without the Alexander Technique in the mix, because for me, the Alexander principles have been part of the equation for my “balancing act" since I was 20. Considering my peers and family members who haven’t had Alexander principles at their disposal, I would bet good money that I can give credit (lots of it!) to Alexander Technique for helping shape my life, and giving me a way to continue to find that delicate balance.
If you are intrigued by this idea, be sure to visit www.acatnyc.org to find out how you can start learning Alexander principles to help you find more balance in life.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Taking Action: How Does That Work in the Context of the Alexander Technique?
 by Brooke Lieb
by Brooke Lieb
In light of the recent hate crime, the mass killing in Orlando targeting the LGBTQ community on June 12, I thought about what it was to respond with meaningful, integrated action.
What has this got to do with the Alexander Technique? Alexander Technique often emphasizes “non-doing” which can be mistaken for inaction. Non-doing is more about having the time and space to unpack a response to find what may be habitual and automatic, and gain access to a conscious, reasoned response.
Working with this paradigm gives me a way to question the accuracy or validity of my feelings, both those I label as sensations, and those I label as emotions. I can also question the habits I have around using those feelings to guide my behavior and actions. I don’t want to respond to this latest tragedy comfortably or in my familiar and habitual way, I want to respond accurately and in measure with my examined belief systems.
I want to communicate with the people who feel particularly at risk of being targeted because of who they love or how they look, a danger that may be even more in the forefront of their day to day lives, as a result of this recent atrocity. I want to offer my support. But for me, my kind words are empty if my actions and behavior don't have the potential to generate a safer world for them.
I want to show empathy and connect with my friends and loved ones to show that I care about this issue and it breaks my heart that people are being murdered because of some distorted set of artificial values held by others. Those beliefs are what make some of us a threat to others of us.
I saw a number of posts about taking action, as the more impactful response to this latest in a “much too frequent and much too long” string of mass killings.
So I went to google to find out how to take action. I donated to the Brady Campaign, I signed a petition which I was informed was equivalent to writing a letter.
I wrote to both of my state senators to say I am a constituent who supports strict gun control, and when considering the second amendment as written: "A well-regulated militia being necessary to the security of a free state, the right of the people to keep and bear arms shall not be infringed” I support limiting access to and the use of guns to the confines of a well-regulated militia.
So, yes, I have been crying since Sunday, June 12, and looking at my transparent biases and bigotry to take responsibility for the ways I may have inadvertently contributed to the climate in our country by being ignorant and unable to see what I may be a party to. I see that my inaction contributes to the status quo. By the way, I was raised around activists, growing up in the late 60’s and early 70’s, and I take a lot for granted because so many took action during that time in history.
What has this got to do with the Alexander Technique? I am saying “no" to my comfortable habit to remain silent while feeling hopeless. I often keep silent out of my desire to appear non-judgemental and neutral so my clients won’t feel judged in my hands. Silence can be useful in some situations, but silence can also be a way to stay comfortable and ineffective.
So, instead, I am taking action, and being non-habitual by using my literal and literary voice to express my fondest wishes and hopes - that we take the actions needed so we live in a world that values all human life and celebrates creativity and diversity in how we each express ourselves. I wish to live in a world where no one is in danger from another, because of what they have or don’t have, for what they believe or don’t believe. And that we don’t use our personal beliefs to injure each other.
If you want to learn more about some possible actions to take, here are some links:
Contact your congressional representative: http://www.house.gov/representatives/find/
Contact your Senator: http://www.senate.gov/senators/contact/
How did your senator vote on background checks?: http://everytown.org/senate-votes/?source=etno_ETActPage&utm_source=et_n_&utm_medium=_o&utm_campaign=ETActPage
Tweet your congressperson: http://everytown.org/tweet-at-congress/?source=etno_ETActPage&utm_source=et_n_&utm_medium=_o&utm_campaign=ETActPage
Support the Brady Campaign to end gun violence: https://secure.bradycampaign.org/page/contribute/center-enough
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
Returning Home
 by Mariel Berger
Many thanks to my Alexander Technique teachers: Witold Fitz-Simon and Jane Dorlester.
by Mariel Berger
Many thanks to my Alexander Technique teachers: Witold Fitz-Simon and Jane Dorlester.
For a lot of people, sexual intimacy is an attempt to return to our bodies and feel whole. We spend so much time in our heads, experiencing life not fully in our bodies, not feeling the integration of our system. There is so much fixation on finding a partner and experiencing intimacy as a way to feel connected and validated. Through Alexander Technique we practice feeling whole so that we don’t need to be in our front bodies grasping for more. We can be aware of our back bodies, our head moving forward and up, neck free, torso widening and deepening, knees moving forward and away. All of the parts create a simultaneous awareness of the whole: one at a time and all together.
A lot of the pain I experience in life comes from a feeling of being disconnected and isolated. There’s a quote I love by Lawrence LeShan, “It is the splits within the self that make for the feeling of being cut off from the rest of existence.” I am slowly learning how to experience myself without all the splits -- to gather all my different sides --shawdowed and bright -- and hold them into a unified whole.
This past winter I was severely depressed and felt as if my Self were fragmented into tiny meaningless pieces. I felt alone in my head, and disconnected from myself, loved ones, or any purposeful connection. My mind was full of vicious and self-loathing thoughts, and I tried to escape the abuse by fleeing from my body and myself and towards someone I was romantically interested in. I have learned, again and again though, that true resolution comes from staying -- creating space for the pain, witnessing it, holding it, and integrating it into my whole self. If I try to reach outside of myself to escape pain, that only takes me further from home.
I recently took a course on Visceral Manipulation, taught by Liz Gaggini. We learned that in order to heal a client’s organ, you must have an attitude of nonchalance and only put some of your attention on the person. The rest of your attention will stay in your body, in the room around you, and beyond. In order to heal another, you must stay whole. If you give too much, you offer the person a fragmented presence, an energy that is coming just from the front of the body -- a grasping, an end-gaining.
This is so true for relationships. When connecting with another person, even someone to whom I’m greatly attracted, I can practice not coming forward into the pull of hormones and craving, but remain in my full body. There is much pleasure to feel just here as I am, inside myself. This is a new and exciting practice, to realize that simply walking around and being inside my body can feel good, especially after the last 5 years of chronic pain and health problems. I am learning how to hold pain as part of the experience, not the only thing. I am learning to accept all the parts of myself, and to hold them in an awareness that is deep and fulfilling.
This past winter I liked someone so much that I lost my awareness of my back body. I fell forward. I fell hard.
And the ironic thing is, I was leaning forward in order to feel a connection -- to return home. But home is back and up into my torso, widening and deepening, my head moving forward and up, my gaze softening, my neck being free.
Here I am again, having remembered, but life is a process of forgetting and remembering, of getting lost in the pieces, and then expanding our awareness to perceive more. Alexander Technique is the gentle practice each day to return to our whole.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/helsinki-sun-headshot.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]MARIEL BERGER is a composer, pianist, singer, teacher, writer, and activist living in Brooklyn, NY. She currently writes for Tom Tom Magazine which features women drummers, and her personal essays have been featured on the Body Is Not An Apology website. Mariel curates a monthly concert series promoting women, queer, trans, and gender-non-conforming musicians and artists. She gets her biggest inspiration from her young music students who teach her how to be gentle, patient, joyful, and curious. You can hear her music and read her writing at: marielberger.com[/author_info] [/author]
Epiphany
Cate9thTerm-Judy
by Cate McNider
As a soon-to-graduate Alexander Technique teacher, my time at ACAT, and why I embarked on this Alexander journey, has crystallized into this realization: I love epiphanies and live for them! I love that moment when ‘I get it’. That is in the direction of the UP for me. That realization is the inner up that supports the physical going up. Getting out of my own way, and allowing my head to go forward and up is what allows the space to receive information from my consciousness. We focus a lot on the physical habits and procedures to enliven our dynamic oppositions in this biomechanical suit we call a body, and it works. What underlies the physical is our curiosity, our innate impulse to rise, to evolve, to discover who we are, to be ourselves. That journey is a process, the process is a journey. It is the best investment we can ever make, to take that journey consciously, to think in activity, to be aware of what we are doing to and with ourselves, and how those habits are reflected back to us in the world.
It is this love of deepening understanding that makes me curious about how can I help this person, this student, realize they are compressing themselves and that they can stop whatever the habit is and dis-cover the un-ease and allow the ease to reveal itself.
Words are always a problem. For example, how I mean these words and how I am crafting them to communicate a feeling to you may not be what you hear or understand, which is where the hands come in to give you an experience of the AT principles and how that applies to you personally. Most of us share some variation of the ‘back and down’, but how that manifests in our neural network is unique and individual. Many books are written about the AT and the authors themselves struggled to various degrees to describe what FM was doing and what the principles point towards.
The quality of the touch is what takes three years to ‘get’, to just begin this ‘teaching’ journey, to allow the energy of the thought to be transmitted to the student’s whole wedded self. The epiphanies come more often after 3 years of study because I am pausing enough, thus more available for what comes through me and to me, the result of ‘getting out of the way’.
And this communal moment of ‘inhibition’ when the teachers hands are on me, and we are thinking together, powerful change occurs. This ability to change is within all of us. If we don’t let go of the old that no longer serves us, we wear it on our body, as the wind shapes the sand, and our lives repeat old outcomes. Breaking out of a cycle of any psychophysical habit is enhanced by practicing the principles and like a run in stockings, it runs both ways.
How you read this is how YOU read this. What I wrote is what I have real-ized. Take your own trip and find out for yourself!
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/McNider.jpeg[/author_image] [author_info]CATE MCNIDER is in her final term at ACAT and soon to graduate (all requirements being completed)! She has been a bodyworker since 1991, also practitioner certifications in Body-Mind Centering® and Deep Memory Process®. She is a dancer, poet and painter (see youtube). She most recently performed a piece called: ‘Habit and Non-doing‘ at Dixon Place. Her art can be seen at: www.artsicle.com/Cate-McNider and contacted thru her website: www.thelisteningbody.com. Many thanks to all my teachers, volunteer teachers and fellow trainees at ACAT.[/author_info] [/author]
Recipe for Change
 by Patty de Llosa
by Patty de Llosa
Contrast is crucial, bright/dark, sound/silence. We always forget our deep need for quiet as we go thru our day of achieving, solving, hesitating, and wondering if we’ve done all we should. How refreshing a change would be right then, in the middle of the action!
Well, how about it? What if you could stop to listen at any time, over coffee, while brushing your teeth, even at your desk, leaving off focusing on your papers or computer? You could close your eyes and imagine for a moment that there’s another way of functioning. What would you notice? What would you hear? Perhaps your own heart beating and your own soul calling you home.
Unfortunately, without being aware of it, we often allow ourselves to function in an automatic stimulus-reaction mode that leaves no room for conscious awareness. The pressures of life and our habitual patterns rule our choices until it seems nothing new is possible.
However, new findings in neuroscience show that changing how we do what we do is as important for our wellbeing as eating the right food. Studies in neuroplasticity indicate how new impressions stimulate and even feed our neurons. It’s time to celebrate the fact that what we think changes the physical structure of our brain. When we change our minds, we change our brain.
Dr. Jeffrey Schwartz, a practicing neuropsychiatrist affiliated with UCLA, and author of Brainlock, works with people who have obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) by teaching them to change their thinking through a specific four-step program. Well, friends, when you look at it you’ll see that his program could apply to all of us if we want to live more consciously!
The first step is to Relabel your thought, feeling, or behavior—to give it another name. For example that’s what I did some years back when I identified the voice I’d assumed was my conscience to be a tyrannical inner judge (See Taming Your Inner Tyrant). As you recognize and separate out what’s really important to you, you can begin to call some of your drives what they really are, compulsions. They aren’t just another habit, but much stronger, and they live on your energy. In other words, they eat you.
The second step would be to Reattribute what you want to change by calling it by its new name, which could be Automaton, Habit, Tyrant, Mealy-Mouthed Complainer, or any juicy expletive that resonates with you and helps wake you up to its presence.
Dr. Schwartz suggests that the third step, where the real work is, would be to Refocus, replacing your thought or behavior with a new action. What’s more, your brain chemistry will create new patterns of behavior if you can stick at it long enough. As Schwartz explains, “The automatic transmission isn’t working, so you manually override it. With positive, desirable alternatives—they can be anything you enjoy and can do consistently each and every time—you are actually repairing the gearbox. The more you do it, the smoother the shifting becomes. Like most other things, the more you practice, the more easy and natural it becomes, because your brain is beginning to function more efficiently, calling up the new pattern without thinking about it.”
The fourth and final step is to Revalue. As you begin to understand that the old patterns never really worked for you and another way of living is possible, even desirable, the intensity of need for that particular behavior diminishes. You become a happier and healthier human being. This methodology, dear friends, is truly exciting! You can work at any moment to change the chemistry of your brain!
Here are a few exercises you might try:
- Begin to notice which of the demands that come at you in your day you jump to respond, and which you hold back from. Maybe you are like me, good at making to-do lists, but more involved in checking items off than in prioritizing them. When I’m overwhelmed with my list, a couple of questions can help me bring balance to my day: What do I need to do right now? What do I want to do right now? They may not be the same.
- Let it ring. The telephone is our ever-present means of communication with the world. But we don’t have to be its slaves though I sometimes question the intensity of my focus on it. OK, maybe my job is to answer it, but I can begin to take charge of the automaton in me who wants to grab it at the first ring. Try this: Let it ring three times as you allow the sound to penetrate (and perhaps irritate) your newly aware body/mind, then pick it up and respond. Another time, wait two rings, or four. Anything to stay alive to where you are in time and space.
- One way of refreshing your outlook is to take a different route. Whether walking to the subway, driving to the office or taking time for a brisk walk, go a different way, forge a new path. Why does it matter? Ask the nearest neuroscientist!
- When you are at home, the same wake-up-and-live methodology applies. Invite yourself to put on the other shoe first for a week, then change back. Use your other hand to pour the coffee or hold the knife or fork.
- Finally, the uber neuro-improvement challenge will be to experiment with writing with your other hand. Becoming ambidextrous is a royal road to refreshing the brain. So is learning a new language. Investigate crossword puzzles, jigsaw puzzles, brain teasers.
This post appeared originally at Patty de Llosa's blog.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/dellosa.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]PATTY DE LLOSA, author of "The Practice of Presence: Five Paths for Daily Life," "Taming Your Inner Tyrant: A path to healing through dialogues with oneself", "Finding Time for Your Self: A Spiritual Survivor’s Workbook," and co-editor of "Walking the Tightrope: The Jung-Nietzsche Seminars as Taught by Marion Woodman" is a Tai Chi and Alexander teacher who lives and practices in New York City. A contributing editor of Parabola magazine, she has studied many spiritual teachings while making her living as a mainstream journalist at Time, Leisure and Fortune, and raising a family. Visit her blog at www.findingtimeforyourself.com
Ease on Skis
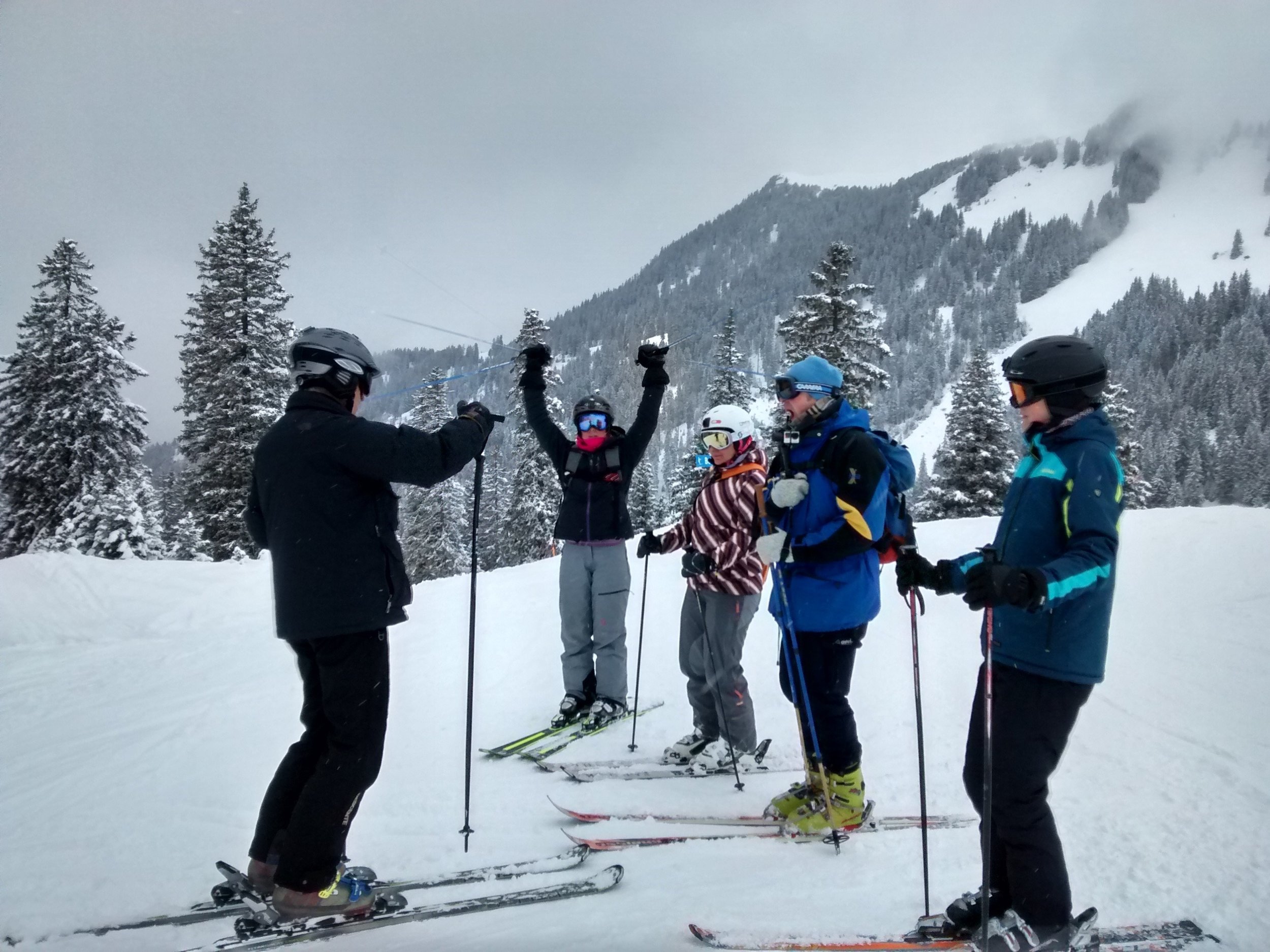 by Emily Faulkner
This past February, I had the good fortune to travel to the Alps to take Erik Bendix’ one week Ease on Skis workshop. I am a passionate skier, and not too bad at it, but having started skiing late in life, I am always frustrated by how slowly I seem to progress and how hampered I am by fear. As a dancer, I love to move. The technique of skiing - the rhythm and the fluid motion – is magical when it comes together, but frustratingly elusive. As soon as I approach a pitch that seems too steep, a patch of ice, or some unexpected bumps, fear takes over, my technique goes out the window, and skiing becomes a matter of survival instead of joy. The Alexander Technique is, of course, the perfect medium by which to analyze fear and response. Enter Ease on Skis!
by Emily Faulkner
This past February, I had the good fortune to travel to the Alps to take Erik Bendix’ one week Ease on Skis workshop. I am a passionate skier, and not too bad at it, but having started skiing late in life, I am always frustrated by how slowly I seem to progress and how hampered I am by fear. As a dancer, I love to move. The technique of skiing - the rhythm and the fluid motion – is magical when it comes together, but frustratingly elusive. As soon as I approach a pitch that seems too steep, a patch of ice, or some unexpected bumps, fear takes over, my technique goes out the window, and skiing becomes a matter of survival instead of joy. The Alexander Technique is, of course, the perfect medium by which to analyze fear and response. Enter Ease on Skis!
Ease On Skis is a combination of a new skiing technique and the application of the Alexander principles to skiing. There is a general methodology to skiing, but there are infinite variations in how different skiers approach the specifics. The most unique aspect of Erik’s approach, it seems to me, is how tall he asks you to stand. One thinks of skiers in a deep monkey, but to watch Erik ski is to see something entirely different. Erik has a unique style of skiing that is much more elongated and upright than any skier I’ve ever seen. It reminds me of how one works on a flying trapeze. In order to maneuver on a small bar hanging in space from ropes, you need to extend your limbs and torso. You need to really spread out in order to counterbalance your body, from head to feet and use it like a long lever. Erik dances down the mountain like a trapeze artist. His basic technique is the same as any good skier – transfer the weight from one ski to the other and glide, like ice skating – but the manner in which he accomplishes this, his speed and power, come from a place of ease, length and balance as opposed to compression and strength.
The way Eric teaches is, of course, quite unique, and we did a lot of interesting exercises both on and off the slopes. We practiced falling and getting up again with and without skis. Skiing is basically controlled falling, so it is helpful to get comfortable with actually falling. We examined walking and turning to see how we can allow our heads to lead our body into a graceful curve around a corner. We examined breath to see how the breath can contribute to a graceful turn. We rolled on the ground allowing the body to spiral, as opposed to rolling in one piece like a log. This helped us access our spirals when we got on the slopes. One exercise that was particularly interesting and satisfying was twisting. While skiing down a slope, you slowly turn your head to one side or the other and then patiently wait for the twist to make its way down to the feet and skis in order to turn. Thus by turning your head and merely allowing the body to follow, you inhibit almost all doing and simply allow yourself to turn.
The week of the workshop happened to be particularly foggy and so I, coincidentally, have an entirely new relationship to the fog. Having calmly directed for a week in fog, I actually sort of enjoy the fluffy comfort of being enclosed in white, and I associate it with the Alexander Principles.
By the end of the week, my fear reflex had dampened considerably. I’d had ample opportunity to breath, relax and direct while careening down a slippery hill, and I was starting to trust my new calmer responses. The internal voice saying, “you are safer and happier when you use the Alexander principles” was finally stronger than the voice saying, “at all costs, hold on tight, and just don’t get hurt!” what Eric calls “crisis management.” From the lens of the Alexander Technique, I also had the opportunity to consider my whole approach to skiing. I love the feeling of skiing, and I love the sociability of it, but if it is so hard for me to become the sort of skier I want to be, can I still enjoy skiing? Watching one of my fellow participants really helped clarify that. She didn’t have particularly impressive technique, but she was calm, she looked with her head and let her skis follow, and low and behold, her skis turned, and she negotiated all sorts of challenging terrain. And she did it quite joyfully. As with all Alexander discoveries, sometimes you realize you need to examine your goal, and sometimes you discover an option you hadn’t realized existed.
About a month after the workshop ended, I happened to go skiing again in the Spanish Pyrenees with my nine-year-old daughter. I was a little frustrated with my technique, but I must say that I felt pretty safe. My habitual feelings of fear were far less than they had been. Skiing in new terrain with my friends and family is my goal, and it was awesome! The Ease On Skis workshop was filmed so hopefully in the next year or two, Erik’s technique will be on display for all.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/e.faulkner.png[/author_image] [author_info]EMILY FAULKNER graduated from the American Center for the Alexander Technique in New York City in 1999, and has been an AmSat certified teacher ever since. Faulkner is also a dancer, dance teacher and choreographer.She is on the faculty of Movement Research, a world renowned institution for experimental dance, and has presented her choreography nationally and internationally. Her most current project is a dance film using Steady Buckets players. Emily teaches privately in New York City, and can be found at emilyfaulkner.com. Email her at emily.a.faulkner@gmail.com. [/author_info] [/author]
I Have Time
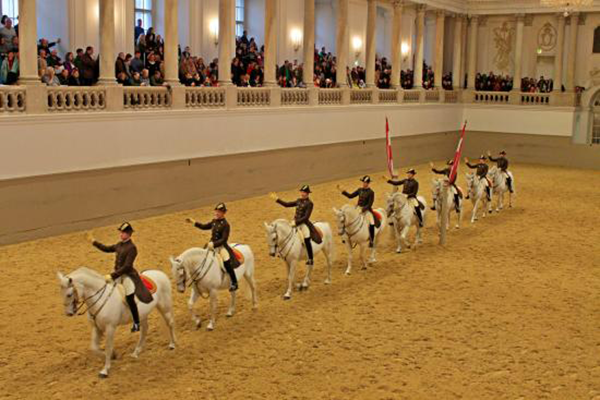 by Patty de Llosa
Hurrying speeds us away from the present moment, expressing a wish to be in the future because we think we’re going to be late. To counter it, Master Alexander teacher Walter Carrington told his students to repeat each time they begin an action: “I have time.” He tells us that on his visit to the Spanish Riding School of Vienna, where horses and riders are trained to move in unison, the director ordered the circling students to break into a canter, adding, “What do you say, gentlemen?” And they all replied together, “I have time.” Try it yourself sometime when you’re in a hurry. Send yourself a message to delay action for a nano-second before jumping into the fray.
by Patty de Llosa
Hurrying speeds us away from the present moment, expressing a wish to be in the future because we think we’re going to be late. To counter it, Master Alexander teacher Walter Carrington told his students to repeat each time they begin an action: “I have time.” He tells us that on his visit to the Spanish Riding School of Vienna, where horses and riders are trained to move in unison, the director ordered the circling students to break into a canter, adding, “What do you say, gentlemen?” And they all replied together, “I have time.” Try it yourself sometime when you’re in a hurry. Send yourself a message to delay action for a nano-second before jumping into the fray.
We are bombarded all day long by stimuli that call us to immediate action. But the pause of saying “I have time” summons an alternative mode of the nervous system, inhibiting the temptation to rush forward under the internal command to “do it now!” When you hold back your first impulse to go into movement by creating a critical pause during which your attention is gathered, you become present to the moment you are living.
So why do we feel the need to hurry? It may be an unconscious sense that danger is near, but it’s not a lion in the street — more likely a deadline or an exam or an unpleasant confrontation. In my case it was often the fear that I wouldn’t finish the job soon enough or well enough to please someone in authority. I discovered that I harbored a Stern Judge who kept an eye on me all day long, commenting on everything I did: “This is more important so get it done first,” or “That’s less important, so hurry through it.” Now, any time I find myself worrying that I don’t have enough time to finish something, I remind myself that I’m creating my own stress. Then I can choose to respond rather than react.
Some people prefer to stay in the fight-or-flight mode, honing their “edge” and paying the price for it in physical fatigue and mental strain. I used to do that too. But even in the middle of the myriad demands to perform at your best, telling yourself “I have time” can provide a mini-break to the nervous system. It offers a moment of choice in spite of the fact that you have to finish the job. It reminds you to attend to your body-being as you press forward with your work, inviting you to release the tensions gathered at the back of your head, and let your thoughts latch onto your body movements. You can interrupt whatever you are doing for just a second to stretch out of the position you are in and into the present moment.
You may well ask, “How can I be expected to stay in the present moment when I’m pressured to finish this job?” O.K. When you have to get something done in a hurry and there’s no choice, try any of these five steps I offer up from my own experience.
First, acknowledge how you really feel about the job. Let your reactions appear in your conscious awareness. Accept them, whatever they may be. “That’s how it is at this moment.”
Second, turn to the only remaining place where there’s freedom: within yourself. Notice the thoughts that are athinking in you and turn them toward the job at hand.
Third, focus your attention on the moves your hands are making — feel the tap of each finger on the computer, or sense the strong muscles that press the freshly glued object together, or revel in the warmth of the soapy water you are washing something in.
Fourth, begin to explore other parts of your body, starting with the back of your neck, where stress tightens our muscles into tough guide-ropes that pull the head out of alignment. Let your thought move whenever and wherever the body moves, seeking out the tense corners and inviting them to release.
Fifth, from time to time interrupt whatever you’re doing, no matter how important, to get up if you are sitting, or at least stretch out and away from the position you are in. If you are standing, think of your legs like tree trunks and send down imaginary roots to ground yourself on the earth while your head floats up above your torso.
Since everything’s connected in the mind-body continuum, you might be surprised to what extent you can relieve your stressed-out system with a brief, non-essential walk down the hall, a peek out the window at the larger world, or even give a seriously deep sigh that engages you right down to the toes. Do anything to interrupt the deadening bond that glues all your attention to what you’re writing, reading, cooking, chopping, building. Truly, the body possesses wisdom that thought doesn’t understand. We can practice listening to it and allow ourselves to expand into present reality. “I have time” helps us do just that.
This post appeared originally at Patty de Llosa's blog.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/dellosa.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]PATTY DE LLOSA, author of "The Practice of Presence: Five Paths for Daily Life," "Taming Your Inner Tyrant: A path to healing through dialogues with oneself", "Finding Time for Your Self: A Spiritual Survivor’s Workbook," and co-editor of "Walking the Tightrope: The Jung-Nietzsche Seminars as Taught by Marion Woodman" is a Tai Chi and Alexander teacher who lives and practices in New York City. A contributing editor of Parabola magazine, she has studied many spiritual teachings while making her living as a mainstream journalist at Time, Leisure and Fortune, and raising a family. Visit her blog at www.findingtimeforyourself.com
From the ACAT Faculty: “What is my Alexander Teacher doing with her hands? It’s not like anything I’ve experienced before…” by Brooke Lieb
 by Brooke Lieb
When I was taking private lessons, I had no idea how my teacher was facilitating changes in my sense of ease and freedom, I just knew it was different from anything I had ever experienced. I recognized some of it was what what she told me to think and wish for, but it seemed most of the changes were the result of some mysterious and magical quality in her hands.
by Brooke Lieb
When I was taking private lessons, I had no idea how my teacher was facilitating changes in my sense of ease and freedom, I just knew it was different from anything I had ever experienced. I recognized some of it was what what she told me to think and wish for, but it seemed most of the changes were the result of some mysterious and magical quality in her hands.
I decided to give the man I was dating at the time, an Alexander “lesson." I had him lay on the floor and I copied what I thought my teacher was doing. Afterwards, all he noticed was that his shoulders weren’t pulled up around his ears anymore. Other than that, nothing much happened and I realized I had no idea what my teacher was doing with her hands. I began to take private lessons with other teachers as well, and it became clear they had all been trained to use their hands in a specific way. There were differences in the quality of their hands, but the ideas and thought process was the same and I recognized the changes that I experienced with different teachers.
When I started teacher training, I was relieved and delighted to discover that teaching would be an extension of the same skills I had been learning as a private student, and these skills would be applied in a practical, step-by-step process, to the use of hands and all the activities of teaching.
I have now been training teachers on the ACAT Faculty since 1992 and while each graduate has a unique quality to their touch, they are also able to facilitate the same response in my system when they have hands on me as my other teachers. The use of the hands is a skill that can be taught.
A Skill That Can Be Taught
In his book Freedom to Change, Frank Pierce Jones writes:
"F. M. told me that in 1914 he was just beginning to find a new way of using his hands in teaching. By applying the inhibitory control (which had proved so effective in breathing and speaking) to the use of his hands he was learning to make changes in a pupil that were different from ordinary manipulation or postural adjustment."
Throughout my training at ACAT, I was taken through a series of activities where I was touching objects, including a hat maker's head form, balls, cups, common objects, a phone book, and a stool. These activities were preparing me to use the same inhibitory control Alexander referred to when using his hands to teach.
My task was to practice my skills of inhibition and directing during these highly stimulating activities, while the teacher lifted or moved the object with her or his hands over mine. I learned how to avoid unneeded (but very habitual) tension in my hands, wrists, arms, legs and back as I allowed the teacher to do the work. I became increasingly able to allow myself to remain empty of intention and habitual tension as the teacher acted upon the object. I was merely the observer.
As I mastered this ability to follow the leader, I was given more and more responsibility for taking over lifting and moving these objects myself. I continued to override my habit of excess effort and tension and the objects felt lighter and easier to move.
This was the model I was taught to use my hands in teaching: recognize my habit of stiffening or tensing throughout my body to use my hands; pause to give myself time to reduce the level of effort I bring to the task; and use my intentional thinking to carry out the task in a more easeful way, with tone and effort distributed more easily throughout my body.
I use this step-by-step method throughout a lesson, and it is how I train teachers to develop their own step-by-step methods for themselves.
Lifting A Head
A practical example: Adjusting the height of books under a student's head during a table lesson.
This task involves lifting and supporting the weight of a student's head with one hand while adding or removing books with the other.
My first strategy is to spend as little time as possible weight bearing while still accomplishing the task. At strategic moments along the way, I give myself time to pause and release the bracing and effort that arises from anticipating and then actually lifting.
- I roll my student's head to one side or the other. The books are still supporting the weight of the student's head.
- I rest the hand that will lift her or his head on the books and let the back of that hand release onto the book. This helps me interrupt my tendency to grasp the student's head with tension.
- I roll the student's head onto my hand, and give myself time to refrain from lifting. Instead, I keep resting my hand on the books with the stimulus of my student's head on that hand. This moment of inhibition is valuable for me and for the student.
- I consider lifting the student's head and observe where I want to brace in anticipation of lifting. I undo the preparation I have observed, since I am not yet lifting. This allows me to actually lift with less anticipatory and wasted tension.
- As I lift, I continue to think in ways that allow me to minimize effort and tension as I support the weight of my student's head.
- I change the height of the books with the other hands as I continue the thinking process described in step 5.
- I return my hand to rest on the new book height, and take time to let my student's head rest in my hand, letting go the effort of weight bearing.
- I use my available hand to gently roll the student's head off the hand that did the lifting.
- I roll the student's head back to center.
The American Center for the Alexander Technique (ACAT) runs the oldest Teacher Certification Program in the United States and is proud to have trained more than a third of the country’s Alexander Technique teachers, taught by our world-class faculty. ACAT also serves as a membership organization for Alexander Teachers and students. To find out more about the program click here or come to our Open House May 2, 7:00pm to 9:00pm.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Brooke1web.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]N. BROOKE LIEB, Director of Teacher Certification since 2008, received her certification from ACAT in 1989, joined the faculty in 1992. Brooke has presented to 100s of people at numerous conferences, has taught at C. W. Post College, St. Rose College, Kutztown University, Pace University, The Actors Institute, The National Theatre Conservatory at the Denver Center for the Performing Arts, Dennison University, and Wagner College; and has made presentations for the Hospital for Special Surgery, the Scoliosis Foundation, and the Arthritis Foundation; Mercy College and Touro College, Departments of Physical Therapy; and Northern Westchester Hospital. Brooke maintains a teaching practice in NYC, specializing in working with people dealing with pain, back injuries and scoliosis; and performing artists. www.brookelieb.com[/author_info] [/author]
The Zen Coach
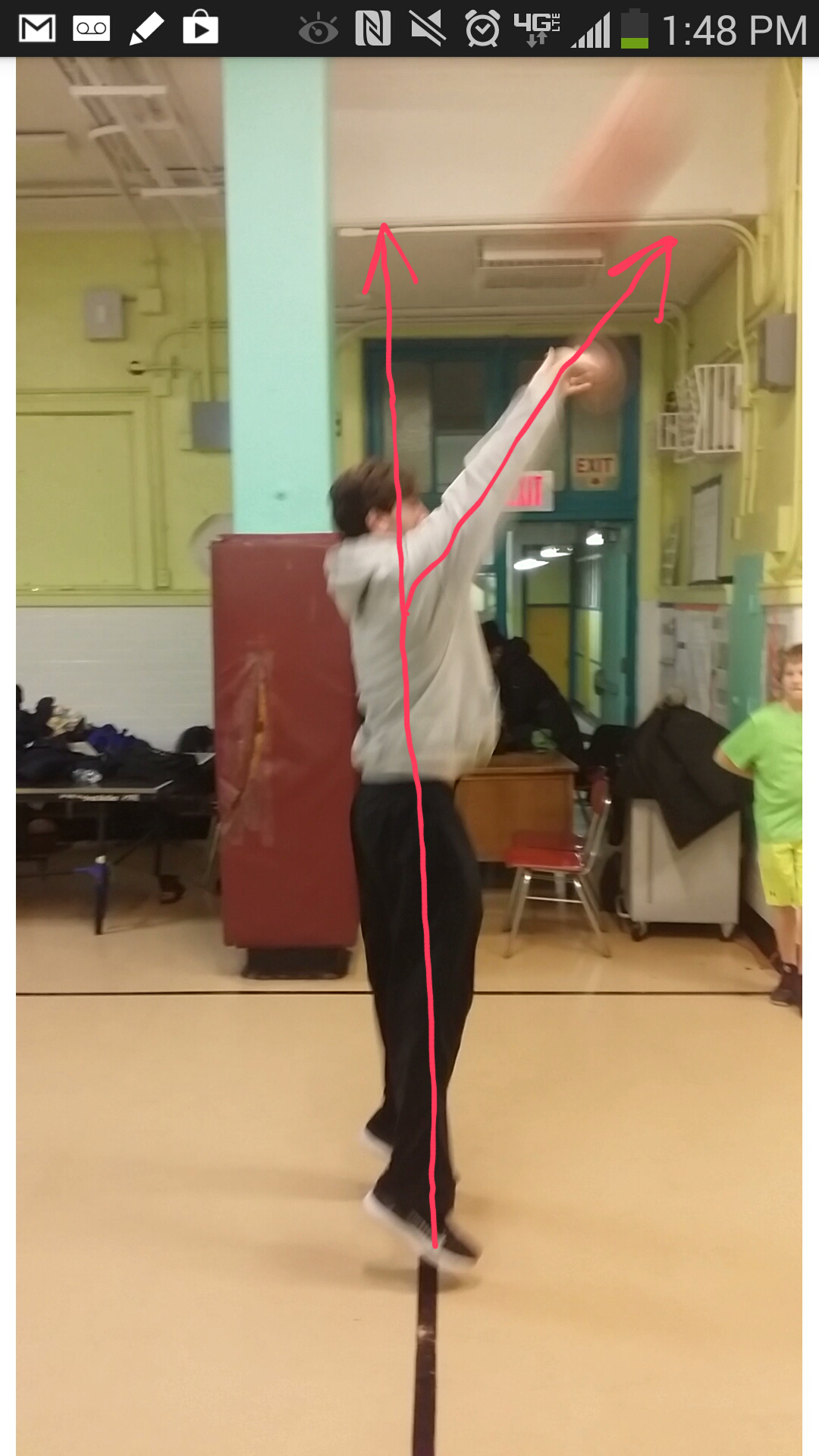 by Emily Faulkner
by Emily Faulkner
I have the privilege of being the movement coach for Steady Buckets, a youth basketball league in New York City that serves kids ages 6-18. It’s a free program that offers skill building classes as well as league play. Children from all walks of life come to this program, from Manhattan’s elite private schools to the projects in the Bronx. I owe this opportunity to the visionary coach, Macky Bergman, who saw that the Alexander Technique would reinforce his coaching, but from a completely different angle.
About two years ago, Macky and I sat down for coffee, and I explained to him why I wanted to work with his players, and how the Alexander Technique would help them. Two hours later, after popping up and down to demonstrate for each other monkey, defensive stance, and proper shooting form, we were both brimming with excitement. Macky is a tough-talking coach, but he’s open minded and interested in alternative techniques to help his players focus and be present. He brought in a Tai Chi teacher one year. Macky intuitively understood inhibition: in order to get the ball through the hoop, you need to let go of the desire to get the ball through the hoop. Additionally, he was frustrated that he couldn’t get the kids to shoot with a straight spine or stand upright when defending. As a dancer and an Alexander teacher, it was pretty clear to me that the kids needed to use their hip joints. It was a perfect marriage: For Macky, what could be better than someone who would enable his players to improve their form? For me, what could be better than an unlimited supply of kids to whom I could teach the Alexander technique and see proof positive that the AT can change lives and games?
After working with Steady Buckets for two years, I’ve made many observations. Although the Alexander Principles are always the same, the bodies that come to me vary wildly. Some kids are slack; some kids are tense; some kids try too hard; some don’t try at all. I usually teach one on one, and give about ten kids, a 5-10 minute lesson each. Certain kids absorb the technique like a sponge and instantly see what it can do for them. They start making their shots and finding themselves “in the zone.” “I feel loose. I feel light. I couldn’t miss.” Kids who are in pain often see the value immediately. Some kids don’t see the value, and I let them go. It’s not for everyone. The principles are the same, but the challenge each kid faces is unique.
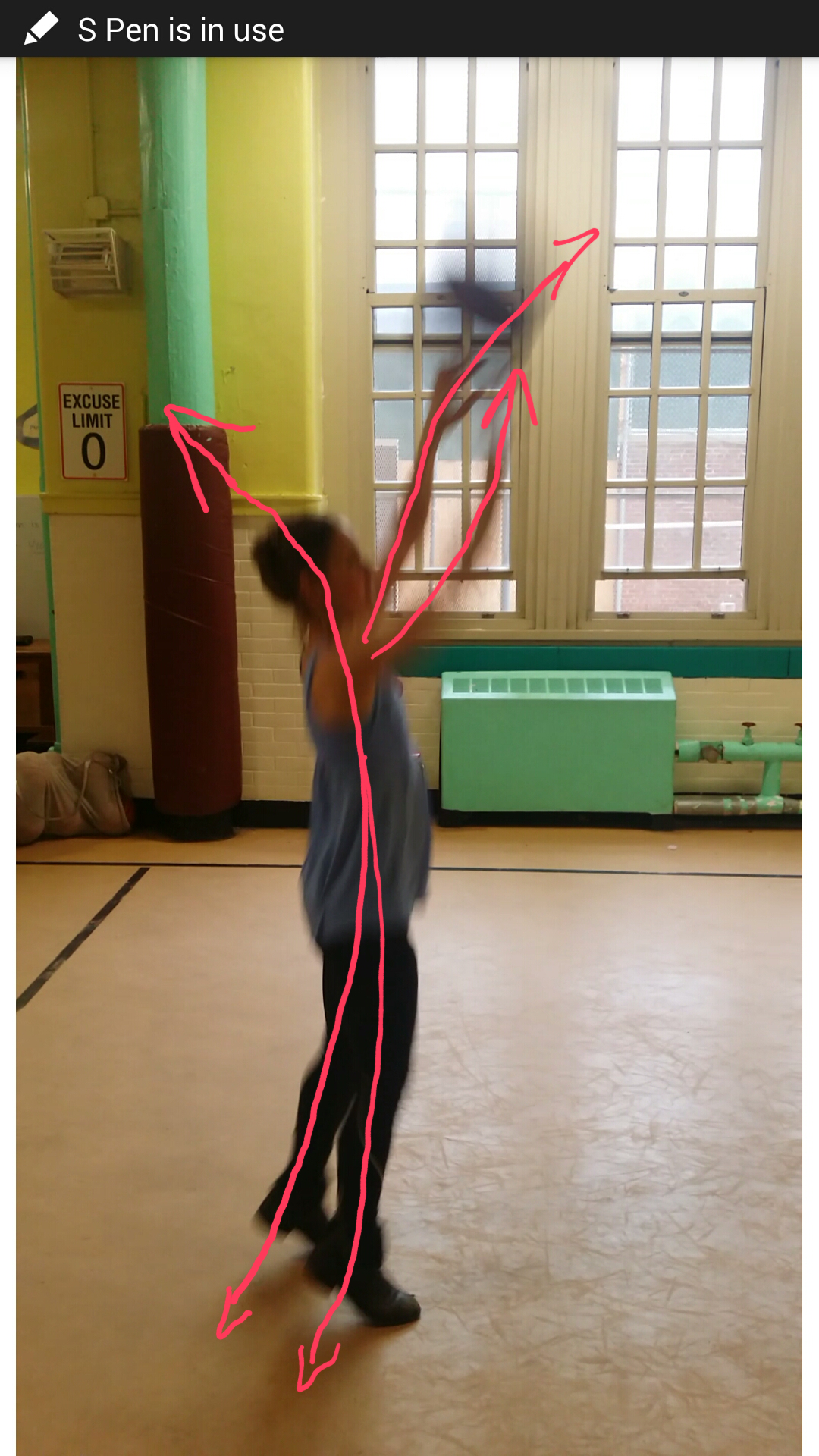
We do a lot of monkey because it is the base for shooting, dribbling, defending, everything actually. I incorporate a lot of Dart practices, like spirals and curves, and the innate springiness of the body. Depending upon the age of the kid, I use analogies like a river running up through the body, or that the floor bounces us up like a ball from our feet through the rest of the body. I show them that their arms can move independently of their torsos by folding at the gleno-humoral joint, and this starts to help them to see that when they shoot, their torsos can remain full and upright even as their arms move. For someone who doesn’t play any sports, I have an impressive theoretical knowledge of shooting form. My goal is to consistently hit foul shots, and be one of those rare experts who gained mastery from a completely different angle. But even with the Alexander Technique, it takes a tremendous amount of practice, and I haven’t devoted nearly enough time.
I came into this thinking that shooting would be the most obvious application of the Alexander Technique because it is a pure Alexander situation: it involves monkey and inhibition. But now I see that shooting is the most emotionally charged, habitually ingrained skill they learn, and very difficult to change. Proper shooting form involves sending the ball up in the air in a large arc by holding the body vertical, straightening the arms up over the head and slightly forward, and using the power of the jump to propel the ball. See Macky’s lines of force, Exhibit A: up through the whole body, forward through the hands and arms. For the younger kids, it is counterintuitive to do this. They want to fling the ball forward with their elbows counteracted by throwing their upper backs backward because they don’t believe that straightening the arms coupled with a jump up will be enough. See my version of this, Exhibit B. Older kids are deeply attached to whatever form of shooting has been working for them, even if it hasn’t been working well. When they change their technique, they will probably lower their shooting percentage before they raise it. And until the kids are really mature and philosophical about basketball, they don’t shoot a high enough arc because they’re aiming for the basket as opposed to aiming for the center of the hoop above the basket. Teaching someone to prioritize the means whereby in the act of shooting a basket is like asking a hungry person to look at their food for ten minutes before beginning to eat. It takes A LOT of inhibition. They need to truly let go of the goal of making the basket.
Officially, I am the movement coach; a dancer who came to teach the players better posture and better movement patterns. Then I thought perhaps I would call myself the biomechanics coach because it sounded substantial and technical. I’ve come to realize, however, that the main thing I have to offer them is inhibition. The other coaches can teach them form and biomechanics (although they don’t usually understand how to access the hip joints), but nobody else can teach inhibition. I am their Zen coach. I teach them to let the ball shoot itself, to let the game play itself. And as much as they need to learn how to inhibit in order to change their form, I need to inhibit my desire to see them improve. As with any other activity, change can happen both instantaneously and glacially. They fold into a smooth, balanced monkey, and suddenly they’re moving around their opponents a beat ahead of everyone else. When it comes to shooting, they slowly start to trust a different form. One of my favorite students who falls deeply into the category of “tense and trying too hard” improved dramatically when I said, “remember that you shoot better when you’re relaxed.” That phrase allowed him to inhibit.
The Steady Buckets’ motto is “Outwork ‘Em.” The pursuit of excellence requires limitless hours of practice and dedication, and there is no way around that, but to be truly excellent, you must be able to let go of the thing you desire while you work towards it. What a balancing act!
In a more general way, is has been wonderful to share the ability to change. The Alexander Technique shows us that change is possible, and there is a path towards that change. I imagine the kids I work with absorb the idea that they can choose their actions. If they can go from slumping to standing up tall and balanced in less then a minute, maybe some of them will decide to study for a test instead of not study, go to college instead of not going. Maybe some slumped over little kid who considers himself un-athletic will feel “the zone” and decide that he can be good at sports. The Alexander Technique gives us choice and a means whereby!
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/e.faulkner.png[/author_image] [author_info]EMILY FAULKNER graduated from the American Center for the Alexander Technique in New York City in 1999, and has been an AmSat certified teacher ever since. Faulkner is also a dancer, dance teacher and choreographer.She is on the faculty of Movement Research, a world renowned institution for experimental dance, and has presented her choreography nationally and internationally. Her most current project is a dance film using Steady Buckets players. Emily teaches privately in New York City, and can be found at emilyfaulkner.com. Email her at emily.a.faulkner@gmail.com. [/author_info] [/author]
Standing Up Straight Can Be Just As Bad As Slouching
 by Karen Krueger
Many Alexander Technique teachers don't like to even mention the word "posture." They think the very word has so many wrong connotations that it should be avoided. But I take Humpty Dumpty's point of view: the important thing is not what people think a word might mean, but what we say it means:
by Karen Krueger
Many Alexander Technique teachers don't like to even mention the word "posture." They think the very word has so many wrong connotations that it should be avoided. But I take Humpty Dumpty's point of view: the important thing is not what people think a word might mean, but what we say it means:
"When I use a word," Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, "it means just what I choose it to mean—neither more nor less." (Through the Looking-Glass, Lewis Caroll.)
In my opinion, the Alexander Technique does involve posture, but it defines "good posture" and how to achieve it in a very different way than most approaches.
There's no doubt that bad posture is hard on the body. What most people think of as good posture is generally maintained by using excessive muscle tension in the neck, shoulders and back, which in turn stiffens the limbs as well.
If you habitually slouch in your chair, you probably can notice the amount of extra work that is required to "sit up straight" according to the usual idea. On the other hand, if you habitually maintain what you have been taught to believe is good posture, you may not realize how much you are overworking. You have learned to carry yourself stiffly erect as a child, from relatives or teachers. Or perhaps you learned it as an adult, from a physical therapist, a dance teachers or a yoga instructor. Those who taught you to do this had the best of intentions, but the result can be inflexibility, impairment of full breathing and even pain: ironically, the same problems that can result from slouching.
Several of my students have come for lessons with what most people would say looked like good posture, but who had suffered for years from mysterious neck and back pain that could not be traced to any injury or disease. It was immediately apparent to me, with my Alexander Technique lens, that each of them was holding his back and neck ramrod straight, with very tense muscles. As we worked together on letting go of that tension, these students were able to experience being fully upright with much less effort, and the pain gradually disappeared.
Adapted from "A Lawyer's Guide to the Alexander Technique: Using Your Mind-Body Connection to Handle Stress, Alleviate Pain, and Improve Performance."
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/karen-headshot-67.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]KAREN G. KRUEGER practiced law in New York City for 25 years before training at ACAT, and has now been teaching the Alexander Technique for almost five years. She is the author of the recently published book A Lawyer’s Guide to the Alexander Technique: Using Your Mind-Body Connection to Handle Stress, Alleviate Pain, and Improve Performance (ABA Publishing). Website: http://kgk-llc.com. Buy the book.[/author_info] [/author]
A Better Speaking Voice in One Easy (Alexander) Lesson
 by Karen Krueger
I've been reading a lot lately about "vocal fry," a speaking mannerism that some people find extremely annoying and others defend as an innovative trend among influential young women. Vocal fry is a gravelly or creaky sound to the voice that is most clearly heard at the ends of words and phrases. Some people call it "the NPR voice." Others trace it to Kim Kardashian.
by Karen Krueger
I've been reading a lot lately about "vocal fry," a speaking mannerism that some people find extremely annoying and others defend as an innovative trend among influential young women. Vocal fry is a gravelly or creaky sound to the voice that is most clearly heard at the ends of words and phrases. Some people call it "the NPR voice." Others trace it to Kim Kardashian.
People who find vocal fry to be unpleasant and irritating often say it makes the speaker sound frivolous. Others reportedly consider it a mark of authority. Some say that young women cannot expect to be taken seriously in the workplace if they speak this way, and others respond that this is anti-feminist.
I do not propose to join this debate over aesthetics, politics and meaning. However, I would like to weigh in on one thread of the argument. Those who defend their own vocal fry and other trendy vocal mannerisms often say that "it's just the way I talk, and I can't change it." Inevitably, speaking coaches, vocal therapists and other such professionals will chime in with "yes you can, if you take lessons in how to speak properly, and by the way, if you don't, you'll damage your voice in the long run."
I'd like to point out another way: the Alexander Technique.
Anyone who talks can make an immediate change in how her voice sounds by changing what Alexander Technique calls her "use." You can try this out for yourself by duplicating an experiment I tried using the recording function on my phone.
Pick a text to read aloud while recording your voice. First, sit comfortably upright and read a few sentences in your normal speaking voice. Then, slump really badly and continue reading without purposely changing your voice. Next, sit up really straight and stiff, and continue for a few more sentences. Finally, relax and resume sitting easily upright, and read a bit more.
When you play back the recording, I think you'll be surprised by how different your voice sounds in the different parts, especially as you assumed postures different from your normal way of sitting. In my experiment, my "good use" voice (sitting like a good Alexander Technique teacher) was resonant and pleasant, though it had the usual weird otherness that I hear in all recordings of myself. My "sitting up straight" voice sounded unpleasantly strident. And I was very interested to hear that when I slumped, I developed a flat-sounding voice with a distinct vocal fry.
Alexander Technique lessons are good for many things: easing chronic pain, increasing efficiency of movement, dealing with stress, and on and on. I'd like to add to that list that the Alexander Technique can turn vocal fry from something you are stuck with to something you can eliminate -- when and if you choose.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/karen-headshot-67.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]KAREN G. KRUEGER practiced law in New York City for 25 years before training at ACAT, and has now been teaching the Alexander Technique for almost five years. She is the author of the recently published book A Lawyer’s Guide to the Alexander Technique: Using Your Mind-Body Connection to Handle Stress, Alleviate Pain, and Improve Performance (ABA Publishing). Website: http://kgk-llc.com. Buy the book.[/author_info] [/author]
How the Alexander Technique Helps My Vision
 By Jeffrey Glazer
By Jeffrey Glazer
Just like we have habits of movement and thought, we also have habits of how we use our eyes. My habitual eye pattern is called convergence, which means one or both of the eyes tend to be turned inward. In my case, muscularly my left eye converges to the right, and as a result my peripheral vision to the left is partially cut off. But because my convergence is habitual, I’m usually not even aware of its effect on my peripheral vision until I experience a change. To a behavioral optometrist or other keen observer of the eyes, they can see this pattern in me. However, it’s mostly unnoticeable from the outside, but the experience on the inside when it is changed is significant and clear.
While eye exercises can and do help, there is another approach that I use to help remedy this situation. Using my Alexander Technique skill, I am able to let go of neck and upper back tension, which activates better use of my primary control. The primary control is the relationship between the head, neck, and back; the quality of that relationship, for better or worse, affects movement and overall functioning. Once my neck and upper back is freed up from the habitual tension that I employ, my vision changes in the process!
There are two distinct vision changes that occur.
- First, my vision actually becomes sharper. I am nearsighted (myopia), but I notice that I am a little less nearsighted when free from neck and upper back tension. Even with contact lenses or glasses on, the clarity of my vision improves.
- The second change I notice is that the left side of the world seems to open up for me. This is a result of my left eye convergence dissipating. I experience more peripheral vision on the left side and it feels like I have two eyes again.
What astounds me is that I get these results without directly manipulating my eyes. It comes about as an indirect effect of successfully using the Alexander directions (thoughts sent from the brain to the body) to change the quality of my head, neck, and back relationship (i.e. primary control).
This was one of F.M. Alexander’s main points, that to deal with a specific issue we don’t always have to address it directly. Since everything is interrelated, one can get more bang for their buck by working with the whole. And not only does changing the primary control improve my vision, my movement becomes more fluid, breathing improves, my voice is more resonant, my thinking is clearer, and I feel taller and lighter.
In Aldous Huxley’s 1942 book, The Art of Seeing, he writes the following:
“In myopes especially, posture tends to be extremely bad. This may be directly due in some cases to the shortsight, which encourages stooping and hanging of the head. Conversely, the myopia may be due in part at least to the bad posture. F.M. Alexander records cases in which myopic children regain normal vision after being taught the proper way of carrying the head and neck in relation to the trunk.
In adults the correction of improper posture does not seem to be sufficient of itself to restore normal vision. Improvement in vision will be accelerated by those who want to correct faulty habits of using the organism as a whole; but the simultaneous learning of the specific art of seeing is indispensable.” (Huxley 158).
Huxley was a big proponent of the Alexander Technique as well as the Bates method for improving vision. Alexander himself did not approve of specific exercises without attention to the whole self, so his philosophy may differ from Huxley. However, what they have in common is what I know in myself to be true. The restoration of a balanced head, neck, back relationship, and the consequent correction of posture that comes along with it, results in an improvement in my vision.
Bibliography: Huxley, Aldous. The Art of Seeing. Seattle: Montana Books, 1975. Print.
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/jeffrey.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]JEFFREY GLAZER is a certified teacher of the Alexander Technique. He found the Alexander Technique in 2008 after an exhaustive search for relief from chronic pain in his arms and neck. Long hours at the computer had made his pain debilitating, and he was forced to leave his job in finance. The remarkable results he achieved in managing and reducing his pain prompted him to become an instructor in order to help others. He received his teacher certification at the American Center for the Alexander Technique after completing their 3-year, 1600 hour training course in 2013. He also holds a BS in Finance and Marketing from Florida State University. www.nycalexandertechnique.com[/author_info] [/author]
The Alexander Technique: Spiraling Our Lives
 by Mariel Berger
When something is organized it flows in the most efficient way possible. I just moved into a new apartment and am discovering the joy of changing my habits to create a super organized home. Every object has a place, and that place is set up in relationship to all other things so the dynamic of the house flows effortlessly. The apartment itself is small, but its efficient arranging lets everything be seen as a whole, and function to its potential. Just as when our muscular system is integrated well, we are conscious of how the parts relate to each other: one at a time and all together.
by Mariel Berger
When something is organized it flows in the most efficient way possible. I just moved into a new apartment and am discovering the joy of changing my habits to create a super organized home. Every object has a place, and that place is set up in relationship to all other things so the dynamic of the house flows effortlessly. The apartment itself is small, but its efficient arranging lets everything be seen as a whole, and function to its potential. Just as when our muscular system is integrated well, we are conscious of how the parts relate to each other: one at a time and all together.
In this modern world, it is easy to forget about the Whole, since our days are governed by the clock. Linear Time is structured in a way that you can’t see what came before or what will be. We are trapped in seconds, minutes, days --lost in the fleetingness of moments---each one vanishing as we step forward into the next. What if we allowed time to soften from its hard line into a spiral that wraps and wraps around itself? What if we were able to experience time in its Entire Presence?
From years of anxious doing, humans have learned and constructed different patterns from the ones found in nature. Patriarchy, Capitalism, Western Culture--all these very narrow systems have detached us from our true and effortless flow. Just as Corporate Agriculture turned farming into rows, despite the fact that nature’s most efficient growing shape is nonlinear, years of industrious work regimented and fixed our muscles into an unnatural shape. Tension and pain are from habits that are not aligned with nature’s organization.
Western Culture worships lines----------------------------------------------------->
[Linear Time] ---------------------> [GRIDS]-------------------------> [Boxes]------------>
Time in one fixed and narrow arrow always pointing from past to future.
[Lists] [Periods]
[Streets] [Fences]
[Wars] [Watches]
[Patriarchy]
All of these linear forces have tried to grid over nature’s beautiful and miraculous organization--the endlessly flowing spirals moving through every part of life. Spirals are found in all parts of nature: galaxies, hurricanes, whirlpools, nautilus shells, cacti, cauliflower, cabbage, sunflowers, pine cones and even inside us. “Examples of spirals in the human body include the spiral waves of blood flow, twisting curves in bones, and the corkscrew-like umbilical cord.” There are also spirals throughout our muscular system. “The human body is fundamentally built upon spiral design and moves most efficiently in accord with spiral motion.” Carol Porter McCullough via Raymond Dart discusses the “double spiral arrangement of the human musculature” here.
In Alexander Technique we are constantly practicing connecting to the spirals within us, as well as allowing our walk to return to its natural spiral motion. The more we practice Alexander Technique, the more we expand our experience from two dimensional to three dimensional. As our relationship to our bodies shift, our thought process becomes three dimensional, and our experience of time softens from a line into a spiral. Instead of end-gaining or moving in a two dimensional straight line from point A to point B, we find the infinite three dimensional spiral which lets us experience the whole and the parts: one at a time and all together. We allow for our neck to be free, head to move forward and up, torso to widen and deepen, knees to move forward and away, simultaneously and part by part. We pay attention to each piece while remembering the connection to the fluid spiral within and around us.
Just as Alexander Technique organizes our bodies, in Permaculture Design, a practice of efficient and sustainable gardening/farming, we are encouraged to organize our gardens to mimic nature’s shapes. Many people arrange their gardens in spiral pyramid designs. “The Herb Spiral is a highly productive and energy efficient, vertical garden design. It allows you to stack plants to maximise space – a practical and attractive solution for urban gardeners...This Permaculture design maximises the natural force of gravity, allowing water to drain freely and seep down through all layers – leaving a drier zone at the top (perfect for hardy herbs) and a moist area at the bottom for water lovers.” – Adrian Buckley (from here).
Alexander Technique and Permaculture Design are both practices to help the body and land return to an integrative system of parts relating to the whole. Spirals are the essence of nature, and through these practices we organize our bodies and landscapes to resonate with their natural flow. Tiny spirals are in our DNA, pour into our blood, twist into our bones, make up our muscle sheets--and as we walk our arms, hips and torso spiral around our spine. We organize our garden into a spiral of sunflowers and even the sunflowers are endlessly repeating spiraling fractals of themselves. The part is the whole, the whole is the part...and on and on…………Read this piece in any order until you see that the meaning is in every word, and the words combined make meaning. Allow yourself to flow in and out of time, spiralling around and around…..
all together one at a time all together one at a time all together one at a time……..
all together one at a time…….. alltogetheroneatatimealltogetheroneatatimealltogetheroneatatimealltogetheroneatatimealltogetheroneatatimealltogetheroneatatimealltogetheroneatatimealltogetheroneata….…… .... …...
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/helsinki-sun-headshot.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]MARIEL BERGER is a composer, pianist, singer, teacher, writer, and activist living in Brooklyn, NY. She currently writes for Tom Tom Magazine which features women drummers, and her personal essays have been featured on the Body Is Not An Apology website. Mariel curates a monthly concert series promoting women, queer, trans, and gender-non-conforming musicians and artists. She gets her biggest inspiration from her young music students who teach her how to be gentle, patient, joyful, and curious. You can hear her music and read her writing at: marielberger.com[/author_info] [/author]
Create More Ease Walking With The Alexander Technique
by Witold Fitz-Simon Here are two different takes on walking from an Alexander Technique perspective. The first is from ACAT Teacher Training Program faculty member Judith Stern, and the second from first-generation teacher Marjorie Barstow. (Barstow is in her 90's in this video and still going strong!)
https://youtu.be/m6l7F_nrjeM
https://youtu.be/GOMUKfh_bqw
[author] [author_image timthumb='on']http://www.acatnyc.org/main/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/After-crop1.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]WITOLD FITZ-SIMON has been a student of the Alexander Technique since 2007. He is certified to teach the Technique as a graduate of the American Center for the Alexander Technique’s 1,600-hour, three year training program. A student of yoga since 1993 and a teacher of yoga since 2000, Witold combines his extensive knowledge of the body and its use into intelligent and practical instruction designed to help his students free themselves of ineffective and damaging habits of body, mind and being. www.mindbodyandbeing.com[/author_info] [/author]






